另一个博客">
Spring-IoC容器源码导读
1.几个重要类/接口
阅读前的准备
- 源码下载:
- 源码版本:v5.2.1.RELEASE
1.1 BeanFactory 顶级接口(低配版的IoC容器)
BeanFactory接口定义说明
- BeanFactory是低配版的IoC容器,定义了Ioc容器基本的功能
完整版源码:
1 | |
BeanFactory方法属性摘要
1 | |
1.2 HierarchicalBeanFactory接口
完整版源码:
1 | |
HierarchicalBeanFactory方法属性摘要
1 | |
1.3 ListableBeanFactory接口
完整版源码:
1 | |
ListableBeanFactory方法属性摘要
1 | |
1.4 ApplicationContext接口
ApplicationContext接口解析
- 相比于BeanFactory,ApplicationContext是高配版的Ioc容器,其在BeanFactory的基础上实现了更加复杂的扩展功能
- ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory都是BeanFactory的子接口,ApplicationContext继承了这两个接口,ApplicationContext进一步扩展了BeanFactory接口的功能
- . . .
完整版源码:
1 | |
ApplicationContext方法属性摘要
1 | |
1.5 BeanDefination接口
BeanDefination接口定义解析
- BeanDefination用于管理Ioc容器中JavaBean与JavaBean之间的依赖关系,其抽象了Java开发人员对于JavaBean的定义
- Spring将开发人员定义的JavaBean的数据结构转化为内存中的BeanDefination数据结构进行维护
完整版源码:
1 | |
BeanDefination方法属性摘要
1 | |
2.从一个Demo程序开始
2.1 Demo项目配置
maven的pom.xml配置文件
1 | |
2.2 Demo程序
2.2.1启动类
- 代码位置:com.acanx.spring.xml.CspringIocConfigByFileSystemXmlApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
package com.acanx.spring.xml;
import com.acanx.spring.bean.Car;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* ACANX-JavaWeb / com.acanx.spring.xml / SpringIocConfigByXmlFileInClassPath.java
* 文件由 ACANX 创建于 2019/7/30 - 13:39
* Description SpringIocConfigByXmlFileInClassPath:
* 补充说明: 使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext加载文件系统下的配置文件
*
* @author ACANX
* @version 0.0.1.0
* @date 2019/7/30 13:39
* @since 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
*/
public class CspringIocConfigByFileSystemXmlApplicationContext {
private static final Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger(CspringIocConfigByFileSystemXmlApplicationContext.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
logger.info("-------------------");
logger.info(System.getProperty("org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory"));
logger.info(System.getProperty("org.apache.commons.logging.Log"));
logger.info("-------------------");
String location="D:\\ProgramCode\\JavaCode\\ACANX-JavaWeb\\JavaWeb-Spring\\ApplicationContextC.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(location);
Car car = (Car) applicationContext.getBean("myCar");
logger.info(car.toString());
logger.info("Info :{}",logger.isInfoEnabled());
String[] beanNames=applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName:beanNames) {
logger.info(beanName+"::::: "+applicationContext.getBean(beanName).toString());
}
}
}
2.2.2使用到的Bena对象
1 | |
2.2.3 springContext的xml文件ApplicationContextC.xml
1 | |
2.2.4 配置日志 logback.xml(resources文件夹下)
1 | |
3.Spring IOC容器的创建
3.1 进入FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(AbstractXmlApplicationContext抽象类的具体实现类)
- 代码位置: org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
// 上面的this 来到下面的重载构造方法
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent); // 初始化父容器AbstractApplicationContext
setConfigLocations(configLocations); // 设置资源文件的位置
if (refresh) {
refresh();// 核心方法,具体定义在超类AbstractApplicationContext(抽象类)中,是一个模板方法
}
}
3.2 初始化父容器AbstractApplicationContext
3.2.1 AbstractXmlApplicationContext抽象类(FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的父类)
- 代码位置: org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4public AbstractXmlApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
3.2.2 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext抽象类( AbstractXmlApplicationContext的父类)
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4public AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
3.2.3 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext抽象类
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4public AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
3.2.4 AbstractApplicationContext抽象类
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27public AbstractApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
this();
setParent(parent);
}
//上面对应的this()方法
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
//上面对应的 getResourcePatternResolver()方法
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
// this()之后的setParent(parent);方法
@Override
public void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
this.parent = parent;
if (parent != null) {
Environment parentEnvironment = parent.getEnvironment();
if (parentEnvironment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
getEnvironment().merge((ConfigurableEnvironment) parentEnvironment);
}
}
}
3.5 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver类
- PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this)对应的构造方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.java
1
2
3
4
5public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
4.setConfigLocations(String… locations) 方法
- 设置资源文件的位置
4.1 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext.setConfigLocations(@Nullable String… locations) 方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
5. refresh()方法
- AbstractApplicationContext抽象类中定义的refresh()模板方法
- 定义了需要执行刷新操作的一些步骤,只是一个模板,个性化的逻辑由其子类来具体实现
5.1 refresh()方法定义
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 创建BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化Bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
5.2 prepareRefresh()方法
- 正式Refresh()操作前的准备工作
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
// 上述定义的initPropertySources()方法,具体由子类实现
protected void initPropertySources() {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
5.3 obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法
- 创建BeanFactory的核心方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();// 刷新BeanFactory,抽象方法由其子类实现,5.3.1中有说明
return getBeanFactory();// 获取BeanFactory,父类的抽象方法继承并由其子类实现
}
protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
@Override // 该方法在ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中定义
public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
5.3.1 refreshBeanFactory()方法的一种实现
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中的具体实现如下
- refreshBeanFactory()方法是AbstractApplicationContext中定义的抽象方法
- AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中的refreshBeanFactory()方法是该抽象方法的一个具体实现
- 主要作用:刷新BeanFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48// AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中refreshBeanFactory()方法的一种实现
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 检查上下文中是否已存在BeanFactory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
// 存在BeanFactory时先销毁已存在的BeanFactory
destroyBeans();//调用AbstractApplicationContext中的实现
/**
* 以下是AbstractApplicationContext中destroyBeans()方法的实现
* protected void destroyBeans() {
* getBeanFactory().destroySingletons();
* }
*/
closeBeanFactory();// 调用本抽象类中的closeBeanFactory()方法,具体代码在下面列出
}
try {
// 创建新的BeanFactory
// 下面这行代码只会创建一个空的BeanFactory,并未有任何Bean
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);// refreshBeanFactory()方法实现的核心
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
// AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext抽象类中refreshBeanFactory()方法内调用的closeBeanFactory()方法
@Override
protected final void closeBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
//销毁已存在的BeanFactory
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(null);
this.beanFactory = null;
}
}
}
//AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext抽象类中refreshBeanFactory()方法内调用createBeanFactory()方法
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
// 调用下面 AbstractApplicationContext中的getInternalParentBeanFactory()方法
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
AbstractApplicationContext中的getInternalParentBeanFactory()方法
1 | |
DefaultListableBeanFactory的构造方法
1 | |
DefaultListableBeanFactory父类AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory(抽象类)的构造方法
1 | |
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中的customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory)方法
1 | |
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中的loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory)方法
- 是实现refreshBeanFactory()方法的核心
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中定义的抽象方法
1
2protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException, IOException; - 该抽象方法的一个具体实现在org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext中
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext中的loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中定义的抽象方法loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)的一个实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
// 通过上一步创建的空BeanFactory来创建新的XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象
// XmlBeanDefinitionReader用于解析xml文件中定义的bean
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); //
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); //这是一个重载方法,入参是上面生成的beanDefinitionReader
}
new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory)
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory)构造方法调用其父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的构造方法,具体如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// Determine ResourceLoader to use.
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
}
else {
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
// Inherit Environment if possible
if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment();
}
else {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
AbstractXmlApplicationContext抽象类中的initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader)方法
1 | |
AbstractXmlApplicationContext抽象类中的loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader)方法
- 主要功能是解析资源文件的位置
- 调用XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象的loadBeanDefinitions方法解析bean的定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); //具体调用AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中实现的loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources)方法
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);//具体调用AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中实现的loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations)
}
}
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources)方法与reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations)方法
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象的loadBeanDefinitions方法用于解析bean的定义
- reader是XmlBeanDefinitionReader类型的对象,loadBeanDefinitions方法定义在BeanDefinitionReader接口中,
- loadBeanDefinitions方法具体是在AbstractBeanDefinitionReader抽象类中实现的,具体代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int count = 0;
// 遍历每一个资源并依次调用重载方法loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource),定义在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中,具体实现在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中
for (Resource resource : resources) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);//
}
return count;
}
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int count = 0;
//遍历资源数组,调用重载方法loadBeanDefinitions(String location)
for (String location : locations) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location);//
}
return count;
}
count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource)中的loadBeanDefinitions(resource)方法
- loadBeanDefinitions(resource)方法在BeanDefinitionReader接口中定义,具体实现是在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的实现代码如下:
1
2
3
4@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
} - 可以看到,上面的方法又调用了loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource))方法,该方法在BeanDefinitionReader接口中定义,具体实现在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中,具体实现,详细代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
//以流的形式读取资源文件
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
// 调用doLoadBeanDefinitions解析载入文件中的bean定义
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location)中的loadBeanDefinitions(location)方法
- loadBeanDefinitions(location)方法的具体实现AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中;
1
2
3
4
5@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
} - 解析资源文件的路径,得到Resource[]资源数组
- 上面AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的loadBeanDefinitions(String location)方法又调用了同类里面的一个重载方法loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set
actualResources) 具体实现如下: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
//下一行的核心逻辑 调用上面提到的重载方法loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource)
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中的doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)方法
- 该方法是载入定义bean的核心方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
// 解析XML文档
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
// 下面一行代码 注册Bean
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
// 注册Bean的方法
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 注册bean的核心逻辑
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext)
- 功能:
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
// 核心逻辑
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
// registerBeanDefinitions方法中调用的doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for Environment.acceptsProfiles(String...)
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported
// in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details.
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
// 核心逻辑
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
// 上面方法中调用的parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate)对应的方法实现
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
// 本方法的核心逻辑
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
// 上述方法调用的parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);的具体实现
// 根据bean配置的不同,进入不同分支
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
// 本文示例会进入该方法
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
// 上述方法最后进入processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate)后的处理过程:
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
// 注册Bean的关键代码
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils的registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry())方法
- 主要作用:
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReaderUtils
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
// 将Bean的名字和BeanDefinition对象进行注册
// registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());方法定义在BeanDefinitionRegistry接口中:
// 具体实现在中实现
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory中registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
- 作用:
- DefaultListableBeanFactory的字段beanDefinitionMap是一个ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>,用于存储bean的定义信息
- DefaultListableBeanFactory的字段beanDefinitionNames是一个ArrayList
类型数据,用于存储Bean的名称 - 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
// 查找是否存在同名的bean
if (existingDefinition != null) {
// 有同名的bean存在时
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
// 没有同名的bean存在时
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
// beanDefinitionMap存储beanName:BeanDefinition一一对应的K:V信息
// beanName作为key, beanDefinition作为value存入DefaultListableBeanFactory对象的beanDefinitionMap字段中
// 完成Bean的注册,将Bean注册到BeanFactory中
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
// 将所有的beanName保存到beanDefinitionNames字段中,数据类型为
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}- 到此上面的 loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader)方法基本执行完成
- 上一级的loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法也执行到loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader)方法后结束
- 在上述创建BeanFactory的过程中,BeanDefination注册到BeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory)中的类型为ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>,字段名beanDefinitionMap的为对象中
- 向beanDefinitionMap中注册时beanName为key,beanDefination为value;
- DefaultListableBeanFactory对象的字段beanDefinitionNames是一个ArrayList
类型数据,用于存储所有已经注册的Bean的名称 - refreshBeanFactory()方法执行完成,接下来进入其下一行的getBeanFactory()方法
getBeanFactory()方法的一种实现
- AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中getBeanFactory()方法的一种实现
- 获取BeanFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - call 'refresh' before accessing beans via the ApplicationContext");
}
return this.beanFactory;
}
} - getBeanFactory()方法执行完,标志上一级的方法obtainFreshBeanFactory()执行完成,接下来将进入AbstractApplicationContext抽象类中定义的refresh()模板方法中的第三步定义的prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)方法
6 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)方法
- 代码位置: org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
7 postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
- 代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 该方法是一个空方法,具体的实现依据具体的情况在其子类中继承或进行重写
// 观察AbstractApplicationContext到FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(location)的继承路径,其子类中并未实现具体的逻辑;
} - postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)执行完后进入 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法
8. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法
1 | |
- PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List
beanFactoryPostProcessors)静态方法 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
// 上面的方法内部有调用该重载方法
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}
// 上面的方法内部有调用该方法
private static void sortPostProcessors(List<?> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Comparator<Object> comparatorToUse = null;
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
comparatorToUse = ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory).getDependencyComparator();
}
if (comparatorToUse == null) {
comparatorToUse = OrderComparator.INSTANCE;
}
postProcessors.sort(comparatorToUse);
}
9. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);方法
1 | |
- PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate的registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContexs)静态方法,具体代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
//上面的方法内部有调用该重载方法
private static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {
for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
}
}
10. initMessageSource();方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的initMessageSource()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28protected void initMessageSource() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource.
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else {
// Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls.
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource();
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}
11. initApplicationEventMulticaster();方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
12. onRefresh();方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的onRefresh()方法
1
2
3
4
5protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// 该方法是一个空方法,具体的实现依据具体的情况在其子类中继承或进行重写
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
13. registerListeners();方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的registerListeners()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
14. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)方法
- 实例化Bean的核心方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化bean的核心代码
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
// 上一行的preInstantiateSingletons()方法定义在ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口中,
// 具体实现是在DefaultListableBeanFactory中preInstantiateSingletons()方法
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory中preInstantiateSingletons()方法
1 | |
preInstantiateSingletons()方法中调用的getBean方法
- getBean方法定义在BeanFactory接口中
- getBean方法org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory中实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
//下面是上面方法调用doGetBean(name, null, null, false)方法
// 这个方法特别长,以下是完整代码:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 获取当前bean的依赖关系
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
// 根据依赖的beanName递归调用getBean()方法,不断探寻其依赖的bean,直到getSingleton方法返回依赖的Bean,即当前正在创建的Bean
// 直到依赖关系最底层的bean没有依赖对象了,至此整个递归过程结束
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
//
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// getSingleton方法的参数是createBean(beanName, mbd, args)方法的返回值
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
// createBean方法在AbstractBeanFactory抽象类中定义,具体实现是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory抽象类中
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中的createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// createBean方法的核心 该方法会返回Bean对象的实例,具体代码在下面贴出
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
// 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory抽象类的createBean方法中调用的doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args)方法
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建Bean实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 填充bean,实际进行依赖注入的地方
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
// 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory抽象类的doCreateBean方法中调用的 createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args)方法
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
// 调用instantiateBean方法
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
// 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory抽象类的createBeanInstance方法中调用的instantiateBean(beanName, mbd)方法
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
// 核心逻辑
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 核心逻辑
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// 上面的getInstantiationStrategy()方法代码
protected InstantiationStrategy getInstantiationStrategy() {
return this.instantiationStrategy;
}
getInstantiationStrategy()方法的返回接口对象的策略对象的一个实现SimpleInstantiationStrategy
- org.springframework.beans.factory.support.SimpleInstantiationStrategy
- SimpleInstantiationStrategy.instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner)方法的具体实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class<?> clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
// 调用静态方法BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}静态方法BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse)的实现细节
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
// 判断是否是Kotlin类型
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() && KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass())) {
// 是Kotlin类型
return KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args);
}
else {
// 不是Kotlin类型
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ctor.getParameterTypes();
Assert.isTrue(args.length <= parameterTypes.length, "Can't specify more arguments than constructor parameters");
Object[] argsWithDefaultValues = new Object[args.length];
for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) {
if (args[i] == null) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = (parameterType.isPrimitive() ? DEFAULT_TYPE_VALUES.get(parameterType) : null);
}
else {
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = args[i];
}
}
// 调用Constructor的newInstance方法,使用反射创建实例
// 到此之后bean实例创建完成
return ctor.newInstance(argsWithDefaultValues);
}
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());
}
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory抽象类的中doCreateBean方法中调用的populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper)方法
- 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory抽象类中的方法populateBean方法
- 该方法用于填充bean 具体发生依赖注入的地方####################################################################################################################################################33
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for postProcessPropertyValues
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
// 获取bean的所有属性 用于后面配置Property元素 即依赖关系
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 核心逻辑 applyPropertyValues方法的具体代码在下面
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
// 上面方法中调用的applyPropertyValues方法具体代码
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());
}
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
List<PropertyValue> original;
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values.
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<>(original.size());
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
if (originalValue == AutowiredPropertyMarker.INSTANCE) {
Method writeMethod = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName).getWriteMethod();
if (writeMethod == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Autowire marker for property without write method: " + pv);
}
originalValue = new DependencyDescriptor(new MethodParameter(writeMethod, 0), true);
}
// 获取property对应的值 resolveValueIfNecessary方法的代码在下面给出
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
if (convertible) {
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
if (convertible) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try {
// 获取到依赖的对象值后 将依赖值注入
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);对应的方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionValueResolver
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173@Nullable
public Object resolveValueIfNecessary(Object argName, @Nullable Object value) {
// We must check each value to see whether it requires a runtime reference
// to another bean to be resolved.
if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanReference) {
RuntimeBeanReference ref = (RuntimeBeanReference) value;
// 核心逻辑 解决Bean依赖关系 具体代码在下方贴出
return resolveReference(argName, ref);
}
else if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanNameReference) {
String refName = ((RuntimeBeanNameReference) value).getBeanName();
refName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(refName));
if (!this.beanFactory.containsBean(refName)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Invalid bean name '" + refName + "' in bean reference for " + argName);
}
return refName;
}
else if (value instanceof BeanDefinitionHolder) {
// Resolve BeanDefinitionHolder: contains BeanDefinition with name and aliases.
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = (BeanDefinitionHolder) value;
return resolveInnerBean(argName, bdHolder.getBeanName(), bdHolder.getBeanDefinition());
}
else if (value instanceof BeanDefinition) {
// Resolve plain BeanDefinition, without contained name: use dummy name.
BeanDefinition bd = (BeanDefinition) value;
String innerBeanName = "(inner bean)" + BeanFactoryUtils.GENERATED_BEAN_NAME_SEPARATOR +
ObjectUtils.getIdentityHexString(bd);
return resolveInnerBean(argName, innerBeanName, bd);
}
else if (value instanceof DependencyDescriptor) {
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
Object result = this.beanFactory.resolveDependency(
(DependencyDescriptor) value, this.beanName, autowiredBeanNames, this.typeConverter);
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
if (this.beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
this.beanFactory.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, this.beanName);
}
}
return result;
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedArray) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
ManagedArray array = (ManagedArray) value;
Class<?> elementType = array.resolvedElementType;
if (elementType == null) {
String elementTypeName = array.getElementTypeName();
if (StringUtils.hasText(elementTypeName)) {
try {
elementType = ClassUtils.forName(elementTypeName, this.beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader());
array.resolvedElementType = elementType;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Improve the message by showing the context.
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error resolving array type for " + argName, ex);
}
}
else {
elementType = Object.class;
}
}
return resolveManagedArray(argName, (List<?>) value, elementType);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedList) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedList(argName, (List<?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedSet) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedSet(argName, (Set<?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedMap) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedMap(argName, (Map<?, ?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedProperties) {
Properties original = (Properties) value;
Properties copy = new Properties();
original.forEach((propKey, propValue) -> {
if (propKey instanceof TypedStringValue) {
propKey = evaluate((TypedStringValue) propKey);
}
if (propValue instanceof TypedStringValue) {
propValue = evaluate((TypedStringValue) propValue);
}
if (propKey == null || propValue == null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error converting Properties key/value pair for " + argName + ": resolved to null");
}
copy.put(propKey, propValue);
});
return copy;
}
else if (value instanceof TypedStringValue) {
// Convert value to target type here.
TypedStringValue typedStringValue = (TypedStringValue) value;
Object valueObject = evaluate(typedStringValue);
try {
Class<?> resolvedTargetType = resolveTargetType(typedStringValue);
if (resolvedTargetType != null) {
return this.typeConverter.convertIfNecessary(valueObject, resolvedTargetType);
}
else {
return valueObject;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Improve the message by showing the context.
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error converting typed String value for " + argName, ex);
}
}
else if (value instanceof NullBean) {
return null;
}
else {
return evaluate(value);
}
}
// 上面resolveValueIfNecessary方法中调用的resolveReference方法
// 最后获取到依赖的bean
@Nullable
private Object resolveReference(Object argName, RuntimeBeanReference ref) {
try {
Object bean;
Class<?> beanType = ref.getBeanType();
if (ref.isToParent()) {
BeanFactory parent = this.beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent == null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Cannot resolve reference to bean " + ref +
" in parent factory: no parent factory available");
}
if (beanType != null) {
// 发生递归调用
bean = parent.getBean(beanType);
}
else {
// 发生递归调用 根据依赖的名称从BeanFactory中递归得到依赖 最后获取到依赖的bean
bean = parent.getBean(String.valueOf(doEvaluate(ref.getBeanName())));
}
}
else {
String resolvedName;
if (beanType != null) {
NamedBeanHolder<?> namedBean = this.beanFactory.resolveNamedBean(beanType);
bean = namedBean.getBeanInstance();
resolvedName = namedBean.getBeanName();
}
else {
resolvedName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(ref.getBeanName()));
bean = this.beanFactory.getBean(resolvedName);
}
this.beanFactory.registerDependentBean(resolvedName, this.beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof NullBean) {
bean = null;
}
return bean;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Cannot resolve reference to bean '" + ref.getBeanName() + "' while setting " + argName, ex);
}
}
AbstractPropertyAccessor的setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs)方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.AbstractPropertyAccessor
- 循环属性列表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48@Override
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs) throws BeansException {
setPropertyValues(pvs, false, false);
}
// 循环属性列表
@Override
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException {
List<PropertyAccessException> propertyAccessExceptions = null;
List<PropertyValue> propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ?
((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
// 循环属性列表
for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
try {
// This method may throw any BeansException, which won't be caught
// here, if there is a critical failure such as no matching field.
// We can attempt to deal only with less serious exceptions.
// 该方法通过AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor的setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv)方法实现
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
catch (NotWritablePropertyException ex) {
if (!ignoreUnknown) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (NullValueInNestedPathException ex) {
if (!ignoreInvalid) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (PropertyAccessException ex) {
if (propertyAccessExceptions == null) {
propertyAccessExceptions = new ArrayList<>();
}
propertyAccessExceptions.add(ex);
}
}
// If we encountered individual exceptions, throw the composite exception.
if (propertyAccessExceptions != null) {
PropertyAccessException[] paeArray = propertyAccessExceptions.toArray(new PropertyAccessException[0]);
throw new PropertyBatchUpdateException(paeArray);
}
}
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor的 setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv)方法
- 代码位置:org.springframework.beans.AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor########################################################################################################################################
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23@Override
public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
PropertyTokenHolder tokens = (PropertyTokenHolder) pv.resolvedTokens;
if (tokens == null) {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor nestedPa;
try {
nestedPa = getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath(propertyName);
}
catch (NotReadablePropertyException ex) {
throw new NotWritablePropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Nested property in path '" + propertyName + "' does not exist", ex);
}
tokens = getPropertyNameTokens(getFinalPath(nestedPa, propertyName));
if (nestedPa == this) {
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().resolvedTokens = tokens;
}
nestedPa.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
}
else {
setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
}
} - 上面setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv)方法的重载方法setPropertyValue(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8protected void setPropertyValue(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
if (tokens.keys != null) {
processKeyedProperty(tokens, pv);
}
else {
processLocalProperty(tokens, pv);
}
} - processLocalProperty(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv)方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69private void processLocalProperty(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) {
PropertyHandler ph = getLocalPropertyHandler(tokens.actualName);
if (ph == null || !ph.isWritable()) {
if (pv.isOptional()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Ignoring optional value for property '" + tokens.actualName +
"' - property not found on bean class [" + getRootClass().getName() + "]");
}
return;
}
else {
throw createNotWritablePropertyException(tokens.canonicalName);
}
}
Object oldValue = null;
try {
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();//
Object valueToApply = originalValue;//
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(pv.conversionNecessary)) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
valueToApply = pv.getConvertedValue();
}
else {
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor() && ph.isReadable()) {
try {
oldValue = ph.getValue();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof PrivilegedActionException) {
ex = ((PrivilegedActionException) ex).getException();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not read previous value of property '" +
this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
valueToApply = convertForProperty(
tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, originalValue, ph.toTypeDescriptor());
}
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().conversionNecessary = (valueToApply != originalValue);
}
ph.setValue(valueToApply);// 具体代码在下方列出
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent propertyChangeEvent = new PropertyChangeEvent(
getRootInstance(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, pv.getValue());
if (ex.getTargetException() instanceof ClassCastException) {
throw new TypeMismatchException(propertyChangeEvent, ph.getPropertyType(), ex.getTargetException());
}
else {
Throwable cause = ex.getTargetException();
if (cause instanceof UndeclaredThrowableException) {
// May happen e.g. with Groovy-generated methods
cause = cause.getCause();
}
throw new MethodInvocationException(propertyChangeEvent, cause);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent pce = new PropertyChangeEvent(
getRootInstance(), this.nestedPath + tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, pv.getValue());
throw new MethodInvocationException(pce, ex);
}
}
- 上述ph.setValue方法在org.springframework.beans.AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor抽象类中定义
- public abstract void setValue(@Nullable Object value) throws Exception;
- 一个具体实现在org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapperImp的内部类BeanPropertyHandler中,完整代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26private final PropertyDescriptor pd; //BeanPropertyHandler中的字段
@Override
public void setValue(final @Nullable Object value) throws Exception {
final Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());// 找到属性的set方法
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
// 调用Method的invoke方法,完成属性注入
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);//调用Method的invoke方法,完成属性注入
}
} - 至此Ioc容器的启动过程基本结束
15. finishRefresh();方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的finishRefresh()方法
1 | |
16refresh()过程抛出异常时
- 之中有两个处理方法destroyBeans()和cancelRefresh(ex)
16.1 destroyBeans();方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的destroyBeans()方法
1 | |
16.2 cancelRefresh(ex);方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的cancelRefresh(ex)方法
1
2
3protected void cancelRefresh(BeansException ex) {
this.active.set(false);
}16.3抛出异常BeansException
17 resetCommonCaches();方法
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext中的resetCommonCaches()方法
- try-catch-finally代码块中finally包裹的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6protected void resetCommonCaches() {
ReflectionUtils.clearCache();
AnnotationUtils.clearCache();
ResolvableType.clearCache();
CachedIntrospectionResults.clearClassLoader(getClassLoader());
} - 执行到此Ioc容器启动完成,可以正式投入使用
总结
- Ioc的底层原理实现:Spring Ioc启动分为两步:
- 1.创建BeanFactory
- 2.实例化Bean
- Spring的Bean在内存中的状态就是BeanDefination
- 在Bean的创建和依赖注入的过程中,需要根据BeanDefination的信息来递归的完成依赖注入,从代码可以看到,这些递归都是以getBean()为入口的,一个递归是在上下文体系中查找需要的bean和bean的依赖关系;另一个递归是在依赖注入时,通过递归调用容器的getBean方法得到当前依赖的Bean,同时也触发对依赖bean的创建和注入。在对bean的属性进行依赖注入时,解析过程也是一个递归过程,这样根据依赖关系,一层一层的完成Bean的创建和注入,直到当前bean相关的整个依赖链的注入完成。由于整个IoC容器启动过程较为复杂,使用下面的一张图来描述让读者更清楚厘清IoC容器的启动过程。
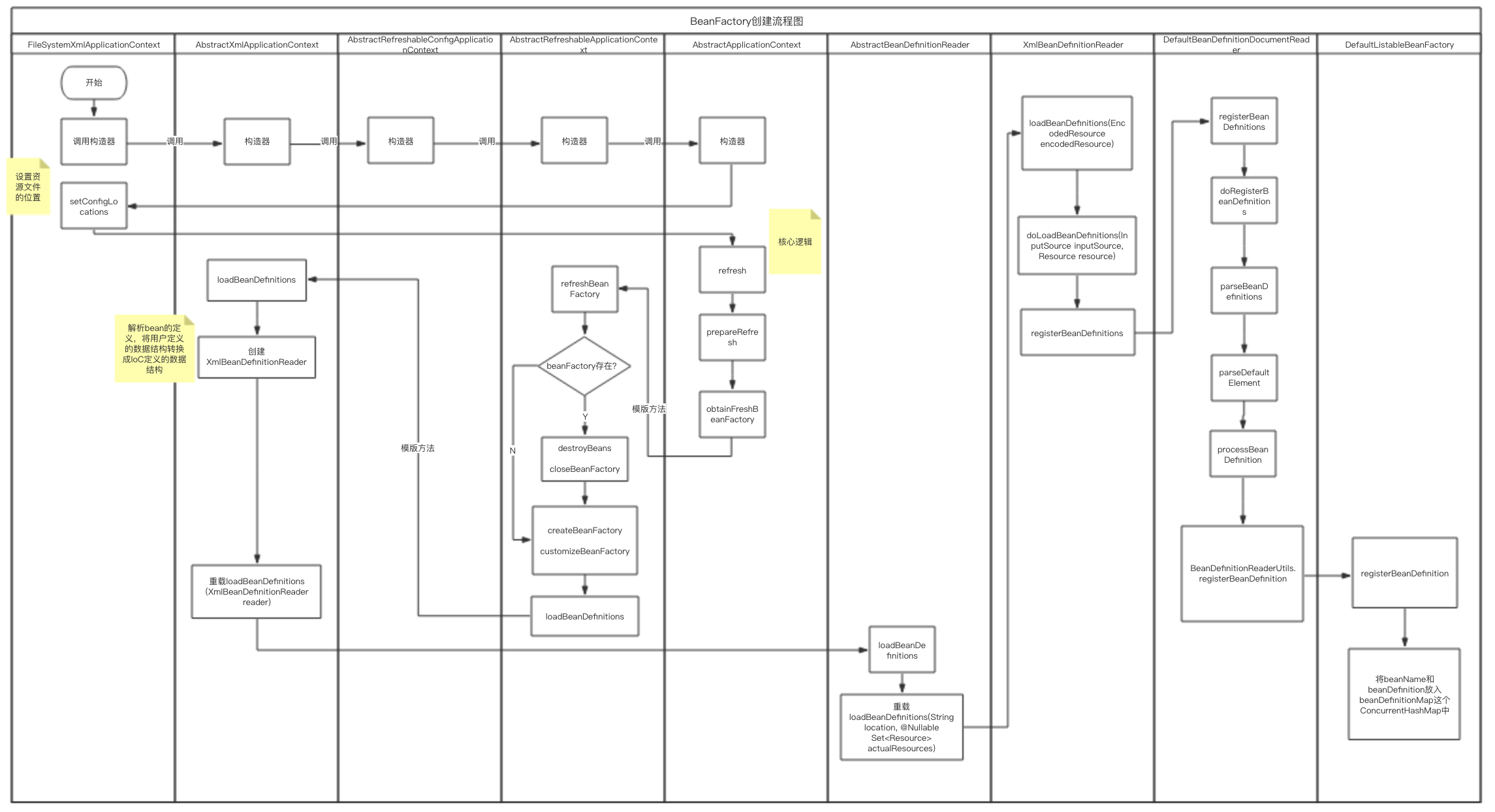
模板
代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
2
3protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}代码位置:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java
1
代码位置:.java
1
代码位置:.java
1
参考资料
- Spring源码深度解析(第二版) 郝佳
- Spring5企业级开发实战 周冠亚 黄文毅 配套源码
- Gitee同步版本:https://gitee.com/ACANX/spring5projectdemo
坚持原创技术分享,您的支持是我前进的动力!